Q. The founder of mycology was
- Linnaeus
- Anton de Berry
- PA Micheli
- None of these
- Anton de Berry
Heinrich Anton de Bary had extensively researched on algae and higher plants and was considered the father of plant pathology. He was also the founder of modern mycology after his contribution to the life history of fungi.
Q. Fungi and disease of Plant was written by
- BB Mundkar
- KC Mehta
- EJ Butler
- None of these
- BB Mundkar
Fungi and Plant Diseases by Mundkur B B
Who wrote the book fungi and plant disease?Sir Edwin John Butler
Q. Agallol is used for
- crop spray
- soil treatment
- seed treatment
- None of these
-
seed treatment
Effects of a mercurial fungicide Agallol 3 widely used for treating sugarcane setts and seed potatoes was studied on Drosophila melanogaster by using parameters such as viability, rate of development, fecundity, hatchability, fertility, and reproductive performance. The chemical was administered by larval feeding.
Q. Late blight of potato is caused by
- Phytophthora infestance
- Physoderma zea-maydis
- Plasmospora viticola
- Pythiurn aphanidermatum
- Phytophthora infestance
Late blight of potatoes and tomatoes, the disease that was responsible for the Irish potato famine in the mid-nineteenth century, is caused by the fungus-like oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. It can infect and destroy the leaves, stems, fruits, and tubers of potato and tomato plants.
Q. Wart disease of potato is caused by
- Olpidium brassicae
- Plasmodiophora brassicae
- Synchytrium endobioticurhe
- Physoderima zea-maydis
- Synchytrium endobioticurhe
Synchytrium endobioticum is a chytrid fungus that causes the potato wart disease, or black scab. It also infects some other plants of the genus Solanum, though potato is the only cultivated host.
Q. Bordeaux mixture was developed by
- Anton de Berry
- EJ Butler
- PMA Millardet
- JC walker
- PMA Millardet
Detail
Pierre Marie Alexis Millardet This book covers the discovery and development of the Bordeaux mixture by Pierre Marie Alexis Millardet. This discovery was significant in the history of plant pathogen control. The Bordeaux mixture was the first fungicide to be widely used throughout the world.
Q. Loose smut of wheat can be controlled by seed treatment with
- Vitavax
- thiram
- agallol
- captan
- Vitavax
Since loose smut fungus totally depends on wheat seed for its survival and carry over from one season to another, growing of disease free seed is the only alternative method of control available at present for large scale adoption. Treat the seed with Vitavax at the rate of 2.5 g per kg of seed before planting.
Q. Fungicides which are absorbed into the system of the plant and move to the remote site of infection are known as
- systematic
- dressers
- systemic
- fungistatic
- systemic
A SYSTEMIC fungicide is a compound which is taken up by a plant and is then translocated. within the plant system, thus protecting the plant from the attack of pathogenic fungi, or. limiting an already established infection.
Q. Hermaphrodite fungi are those in which
- each thallus bears both male and female organs
- some thalli bears only male and some thalli only female organs
- sexually functional structures are produced which are morphologically distinguishable as male or female
- sexually functional structures are produced which are morphologically distinguishable as male or female
- each thallus bears both male and female organs
Fungi in which a single individual bears both male and female gametangia are hermaphroditic fungi. Rarely, gametangia of different sexes are produced by separate individuals, one a male, the other a female. Such species are termed dioecious.
Q. Peach leaf curl is caused by
- Taphrlna epiphylla
- Taphrina klebohnii
- Taphrina deformans
- None of these
- Taphrina deformans
Peach leaf curl is a plant disease characterized by distortion and coloration of leaves and is caused by the fungus Taphrina deformans, which infects peach, nectarine, and almond trees
Q. Powdery mildew of apple is caused by
- Erysiphe polygoni
- Podosphaera leuootricha
- Sphacrotheca fuliginea
- Unclnula necator
- Podosphaera leuootricha
Powdery mildew of apples. Powdery mildew of apples, caused by the fungus Podosphaera leucotricha, affects leaves, buds, shoots and fruits, and forms a dense white fungal growth (mycelium) on the host tissue. The disease stunts the growth of trees and is found wherever apples are grown.
Q. Gene to gene hypothesis of disease resistance and susceptibility was given by
- Erikson
- Flor
- Biffen
- Blaksle
- Flor
Gene-for-gene relationship. The gene-for-gene relationship was discovered by Harold Henry Flor who was working with rust (Melampsora lini) of flax (Linum usitatissimum). Flor showed that the inheritance of both resistance in the host and parasite ability to cause disease is controlled by pairs of matching genes.
Q. The pathogen responsible for Bengal famine was
- Helminthosporium oryzae
- Helminthosporiurn graminearum
- Alternaria alternata
- Curvularia lunata
- Helminthosporium oryzae
The Great Bengal famine was not caused by a crop failure, but was largely due to an increase in urban demand for food during a wartime economic boom that raised food prices for the rura1 poor. The distressing famine in Bengal in 1943-4 caused a gasp of astonishment as well as of horror in India and in the UK.
Q. Sesamum phyllody is caused by
- bacteria
- MLO’s
- viruses
- Fungi
- MLO’s
Phyllody is the abnormal development of floral parts into leafy structures. It is generally caused by phytoplasma or virus infections, though it may also be because of environmental factors that result in an imbalance in plant hormones.
Q.White rust of crucifers caused by Albugo candida belong to class
- Basidiomycetes
- Oomnycetes
- Ascomycetes
- None Of these
- Oomnycetes
Albugo candida commonly known as white rust, is a species of oomycete in the family Albuginaceae. candida is an obligate plant pathogen that infects Brassicaceae species and causes the disease known as white rust or white blister rust.
Q. Which pathogen is associated with the discovery of Bordeaux mixture?
- Plasmodiophora brassicae
- Plasmospora destructor
- Peronospora viticola
- None of the above
- Peronospora viticola
Millardet in 1882 observed that the mixture (called Bordeaux mixture, after the location where it was first used) controlled the severe downy mildew disease of grapes. This discovery marked the true beginning of the modern era of chemicals to control plant disease.
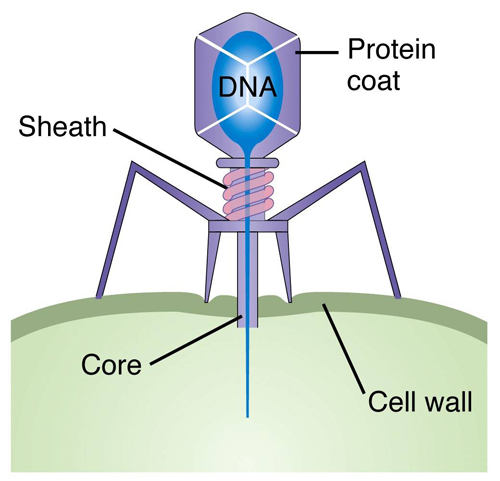
Q. Viruses which can kill the bacteria are known as
- virion
- antibiotics
- Bacteriophages
- None of these
- Bacteriophages
A bacteriophage is a type of virus that infects bacteria. In fact, the word “bacteriophage” literally means “bacteria eater,” because bacteriophages destroy their host cells. All bacteriophages are composed of a nucleic acid molecule that is surrounded by a protein structure.
Q. Green ear disease (downy mildew) of bajra caused by
- Erysiphe graminis
- Albugo candida
- Sclerospora graminicola
- Rhizopus oryzae
- Sclerospora graminicola
Downy mildew or ‘green ear‘ is a very destructive disease of pearl millet in Asia and Africa wherever pearl millet is grown as a food and fodder crop. The disease is soil borne in nature and caused by a fungus Sclerospora graminicola.
Q. Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes are known as
- higher fungi
- lower fungi
- impertect fungi
- None of these
- higher fungi
The main difference between these two groups is in the way in which they produce their microscopic spores. In the Basidiomycetes, the spores are produced externally, on the end of specialised cells called basidia. In Ascomycetes, spores are produced internally, inside a sac called an ascus.
Q. Damping-off of seedlings is caused by
- only Pythium aphanidermatum
- Pythium and Phytophthora sp.
- many fungi including Pythium sp.
- None of the above
- many fungi including Pythium sp.
A soil-borne fungal disease that affects seeds and new seedlings, damping off usually refers to the rotting of stem and root tissues at and below the soil surface. … Several fungi can cause decay of seeds and seedlings including species of rhizoctonia, fusarium and phytophthora.








